Definition:
Beta measures a stock’s volatility versus the market’s volatility. A stock’s volatility is calculated by comparing its return verses that of the overall market return. If a stock’s price does not move in the same direction as the market, it has a beta of zero. A beta above zero means that the stock follows the market. A Beta of 1 means that the stock follows the market very closely If a stock has a negative Beta, then its price moves the opposite direction of the market. The closer a stock is to a negative 1, the more the stock moves the opposite direction of the market.
Example Beta:
If a stock has a Beta of 2.0, it is twice as volatile as the market. If the S&P 500 fell by -10% in a given month, then the stock would be expected to fall around -20%. The stock would also be expected to gain more than the general market during an up market.
Click Here to see all Advanced Stock Trading Articles
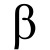
 Greek Referendum Rejects Bailout, Paving The Way To Euro Exit!
Greek Referendum Rejects Bailout, Paving The Way To Euro Exit! Contract
Contract Debt Snowball Method
Debt Snowball Method
