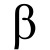Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings), or it can be distributed to shareholders. There are two ways to distribute cash to shareholders: share repurchases or dividends. Many corporations retain a portion of their earnings and pay the remainder as a dividend.
Preferred stock is a special class of stock issued by a company that pays dividends. Preferred stock is more like a bond than true stock because the main appeal is dividend income. Most preferred stocks are limited in the total profit they can earn.
Common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. The terms “voting share” or “ordinary share” are also used in other parts of the world; common stock being primarily used in the United States. It is called “common” to distinguish it from preferred stock.
Three or four characters (usually letters) representing a particular security listed on an exchange or otherwise traded publicly. When a company issues securities to the public marketplace, it selects an available ticker symbol for its securities which investors use to place trade orders. Every listed security has a unique ticker symbol, facilitating the vast array of trade orders that flow through the financial markets every day.
All shares representing ownership of a company, including preferred and common shares.
By law, every year, mutual funds must distribute that year’s net investment income (the total of dividends and interest received, less fund expenses) and net realized gain (gains less losses on securities sales) to its shareholders. These distributions are taxable income reported to the IRS on Form 1099. Investors must report the income on their tax returns. This poses a problem for some mutual fund investors who make initial purchases of mutual funds near the end of a calendar year. Because they receive a capital gains distribution, they immediately receive taxable income and face a mutual fund NAV that is reduced from the distribution.
Profit or loss resulting from the sale of certain assets classified under the federal income tax legislation as capital assets. This includes stocks and other investments such as investment property.
A Call Option gives the holder the right, but not the need to purchase a fixed quantity of a particular stock at a specific price inside a particular time. Call Options are bought by investors who anticipate a price increase.
Stocks of leading and nationally known companies that offer a record of continuous dividend payments and other strong investment qualities.
Trades greater than or equal to 10,000 shares in size and greater than or equal to $100,000 in value.
A measurement of the relationship between the price of a stock and the movement of the whole market. An asset has a beta of zero if it moves are not related to the benchmark’s moves. A positive beta means that the asset generally follows the benchmark, in the sense that the asset tends to move up when the benchmark moves up, and the asset tends to move down when the benchmark moves down. A negative beta means that the asset typically moves in the opposite direction as the benchmark: the asset tends to move up when the benchmark moves down, and the asset tends to move down when the benchmark moves up.
The tendency of the stock market to trend higher over time. It can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities. The opposite of a Bull Market is a Bear Market when the market is moving lower over time.
The tendency of the stock market to trend lower over time. It can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities.
When an option’s strike price is identical to the price of the security. Both call and put options will be simultaneously “at the money.” For example, if the ABC stock is trading at 75, then the ABC 75 call option is at the money and so is the ABC 75 put option. An at-the-money option has no intrinsic value, but may have time value (value if the stock goes up during the period of the option). Options trading activity tends to be most active when options are at the money.
The simultaneous purchase of a security on one stock market and the sale of the same security on another stock market at prices which yield a profit.
When you place an order to buy stocks that must be filled completely, with the total quantity requested, or the trade should not execute at all.
Technical Analysis is the use of technical indicators comprising of statistics using past market information to predict which direction the security price will move.
Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage. The trailing stop adjusts automatically as the price of the security rises and bases itself on the new appreciated value. This type of order allows profits to be made while cutting losses simultaneously.
Margin is the amount of money supplied by an investor as a portion of the total funds needed to buy or sell a security, with the balance of required funds loaned to the investor by a broker, dealer, or other lender.
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is Total net profits divided by the number of outstanding common shares in the market.